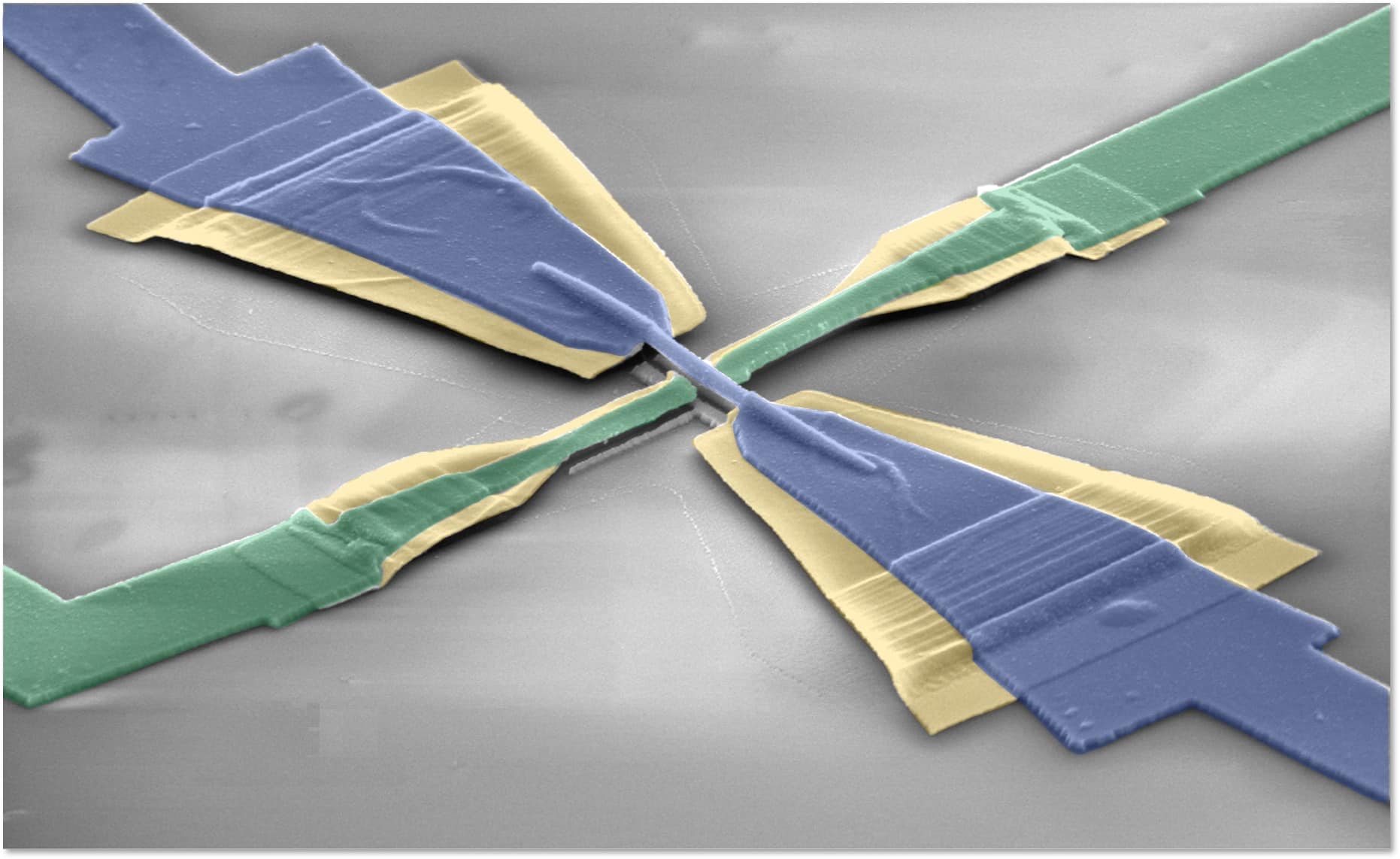
Cnr Nano researchers demonstrates the control of a supercurrent transistor made up of a suspended nanowire, fabricated with an innovative technique. The result, published in the journal ACS Nano by Francesco Giazotto’s group and Lucia Sorba’s group, allows a better understanding of the electrostatic field-effect in superconducting metals.
Under standard conditions, the electrostatic field-effect is negligible in conventional metals and was expected to be completely ineffective also in superconducting metals. This common belief was recently put under question by a family of experiments that displayed full gate-voltage-induced suppression of critical current in superconducting all-metallic gated nanotransistors. To date, the microscopic origin of this phenomenon is under debate, and trivial explanations based on heating effects given by the negligible electron leakage from the gates should be excluded.
In their paper, Francesco Giazotto’s superconductivity group and Lucia Sorba’s nanowire growth group demonstrates the control of the supercurrent in fully suspended superconducting nanobridges. Their advanced nanofabrication methods allows to build suspended superconducting Ti-based supercurrent transistors which show ambipolar and monotonic full suppression of the critical current for gate voltages of VGC ? 18?V and for temperatures up to ?80% of the critical temperature. The suspended device architecture minimizes the electron–phonon interaction between the superconducting nanobridge and the substrate, and therefore, it rules out any possible contribution stemming from charge injection into the insulating substrate. Besides, the finite element method simulations of vacuum electron tunneling from the gate to the bridge and thermal considerations rule out the cold-electron field emission as a possible driving mechanism for the observed phenomenology. Their findings promise a better understanding of the field effect in superconducting metals.
Mirko Rocci, Giorgio De Simoni, Claudio Puglia, Davide Degli Esposti, Elia Strambini, Valentina Zannier, Lucia Sorba, and Francesco Giazotto, “Gate-Controlled Suspended Titanium Nanobridge Supercurrent Transistor”, ACS Nano, https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.0c05355